Admission Controller Lab
Let’s test our admission controller and see if it is working as intented, in this lab we will a deploy two different deployments into different namespaces, one with the admission controller label (spot.io/inject-aks-spot-toleration: true) and one without.
Let’s create two namespaces, one with label and one without. Copy the lines marked with “➜ "
➜ kubectl create namespace admission-test
➜ kubectl create namespace no-admission-test
➜ kubectl label namespaces admission-test spot.io/inject-aks-spot-toleration=true
You should see the result below:
namespace/admission-test created
namespace/no-admission-test created
namespace/admission-test labeled
Lets describe the namespaces to see the difference, first lets describe the admission-test namespace. Run the following : `kubectl describe ns admission-test`
➜ kubectl describe ns admission-test
Name: admission-test
Labels: kubernetes.io/metadata.name=admission-test
spot.io/inject-aks-spot-toleration=true
Annotations:
No resource quota.
No LimitRange resource.
As you can see the label `spot.io/inject-aks-spot-toleration=true` is present here but is missing in the no-admission-test namespace.
➜ kubectl describe ns no-admission-test
Name: no-admission-test
Labels: kubernetes.io/metadata.name=no-admission-test
Annotations:
No resource quota.
No LimitRange resource.
Let's create a simple ngnix deployment and deploy them into different namespaces that we already created.<br>
Create a file `admission-example.yaml` with the following content
```yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: admission-example
namespace: admission-test
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx-dev
image: nginx
resources:
requests:
memory: "100Mi"
cpu: "4"
nodeSelector:
env: ocean-workshop
example: "1"
Run kubectl apply -f admission-example.yaml to create the deployments.
➜ kubectl apply -f admission-example.yaml
deployment.apps/admission-example created
Let’s check if the tolerations were injected properly into the pod, we did not include those in the .yaml file.
Run kubectl get pod -n admission-test
➜ kubectl get pod -n admission-test
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
admission-example-7696b88f47-4x6kt 0/1 Pending 0 26s
Run describe on the pod and review the “toleration” section of the output.
Run kubectl describe pod 'podname' -n admission-test
➜ kubectl describe pod admission-example-7696b88f47-4x6kt -n admission-test
Node-Selectors: env=ocean-workshop
example=1
Tolerations: kubernetes.azure.com/scalesetpriority=spot:NoSchedule
node.kubernetes.io/memory-pressure:NoSchedule op=Exists
node.kubernetes.io/not-ready:NoExecute op=Exists for 300s
node.kubernetes.io/unreachable:NoExecute op=Exists for 300s
You can see the spot required toleration that was not in the original .yaml file was added (kubernetes.azure.com/scalesetpriority=spot:NoSchedule). Lets make sure this pod was also scheduled on SPOT VM.
This is what we can see from the Logs tab in the Spot console.
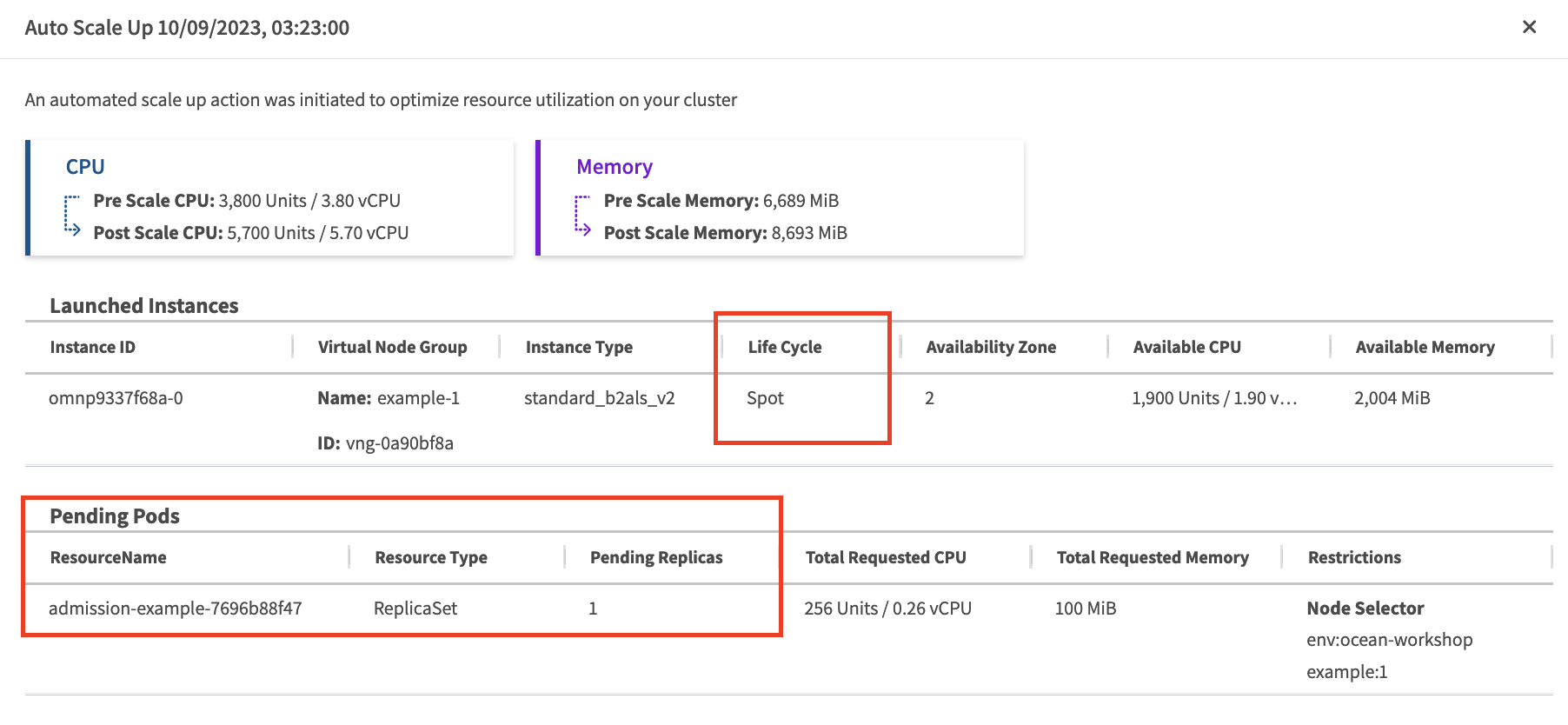
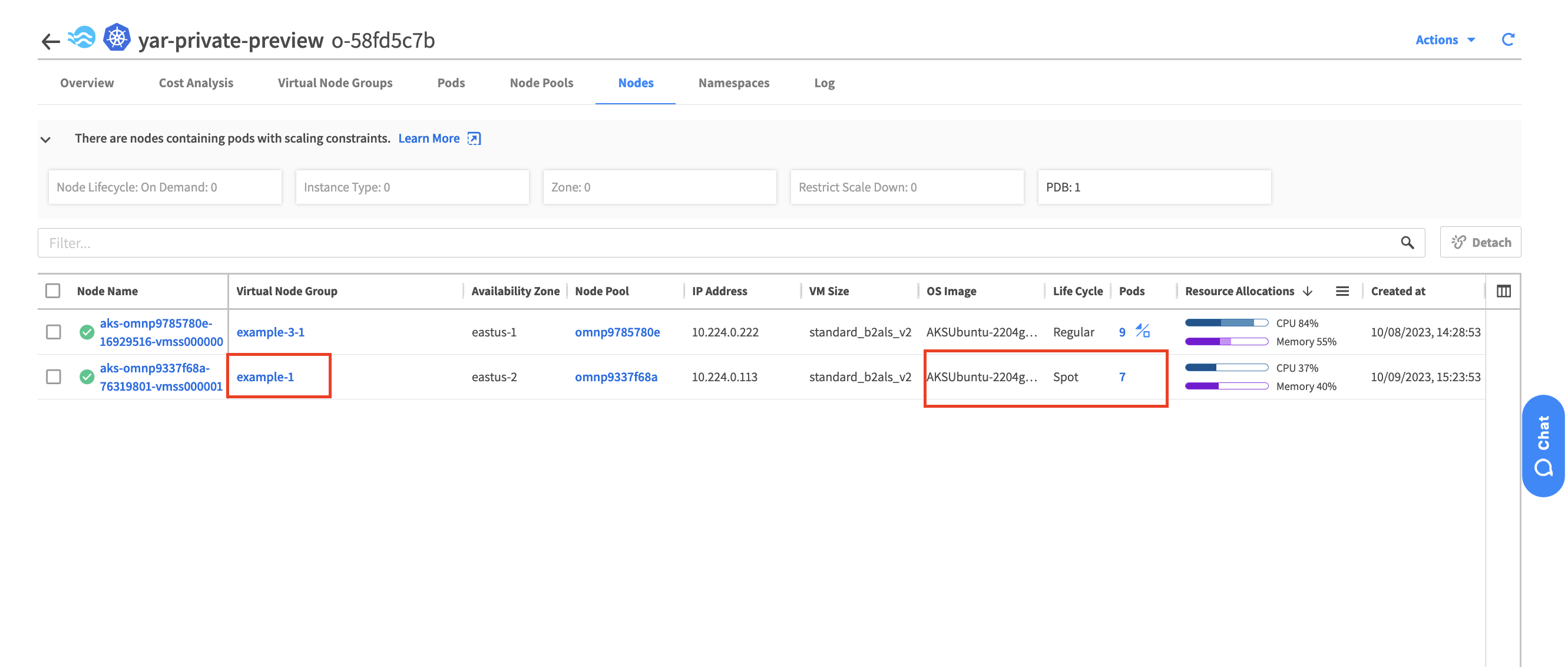
This is what we can see from the Node tab in the Spot console.
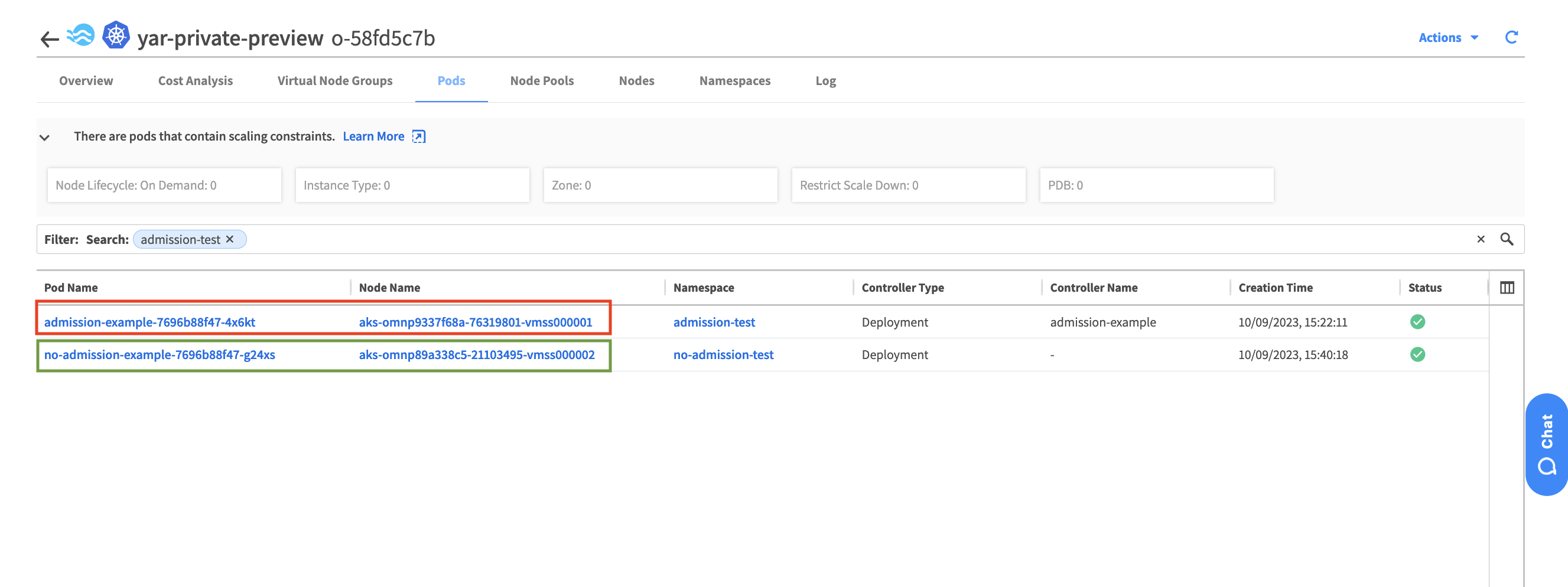
Let’s try to deploy the other ngnix deployment into the namespace that has no admission controller label.
Create a file no-admission-example.yaml with the following content
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: no-admission-example
namespace: no-admission-test
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx-dev
image: nginx
resources:
requests:
memory: "100Mi"
cpu: "4"
nodeSelector:
env: ocean-workshop
example: "1"
Run kubectl apply -f no-admission-example.yaml to create the deployments.
➜ kubectl apply -f admission-example.yaml
deployment.apps/no-admission-example created
The pods are now pending, they are waiting for VM’s to be scheduled on. Run kubectl get pods -n no-admission-test
➜ kubectl get pods -n no-admission-test
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
no-admission-example-7696b88f47-g24xs 0/1 Pending 0 21s
Lets check the toleration of the pod in this namespace, as you can see we do not see the kubernetes.azure.com/scalesetpriority=spot:NoSchedule label. That means that the admission controller did not inject the tolerations.
Run the following : kubectl describe pod 'podname' -n no-admission-test
➜ kubectl describe pod no-admission-example-7696b88f47-g24xs -n no-admission-test
Node-Selectors: env=ocean-workshop
example=1
Tolerations: node.kubernetes.io/memory-pressure:NoSchedule op=Exists
node.kubernetes.io/not-ready:NoExecute op=Exists for 300s
node.kubernetes.io/unreachable:NoExecute op=Exists for 300s
Let’s check the VM’s where the pods are running , as you can see the new pod: no-admission-test was scheduled on different VM then the pod: admission-test. The vm in red is Spot VM while the VM in green is Normal VM.