Elastigroup ITF
What is Intelligent Traffic Flow?
Intelligent Traffic Flow (ITF) is a feature that optimizes the incoming traffic distribution to instances that are launched by Elastigroup. ITF manages in real time the traffic distribution to target groups based on the number of vCPUs (or other user-defined parameters) each target group has.
Overview Description
Elastigroup creates target groups on your behalf, assigns them to the rules that you provide, and continuously calculates and assigns the weights per each target group in the rule. Since the weights are based on the number of vCPUs in the target groups, and traffic is distributed according to the weights, then it is possible to optimize the vCPU utilization in each of the target groups.
Rules Management
You configure ITF as part of the creation or update of an Elastigroup, and during this process you can add one or more rules that all are under the same application load balancer (the rules can be from different listeners within the ALB). After adding a new rule, migration of the added rule will start. Elastigroup always uses a graceful migration process so that the distribution to the current instances is not interrupted.
ITF works only with application load balancers, and each Elastigroup can manage as many rules as you need.
Benefits
- Efficient CPU utilization. Elastigroup ensures the instances of different sizes are all optimized to your configured utilization.
- Increased savings by Elastigroup. When the vCPU is utilized more efficiently, you can reduce the overall compute capacity required to run your applications.
- Focus on application. Previously, you had to manage the distribution in addition to the application. Now you can focus on the application, while Elastigroup takes care of the distribution.
- More flexibility with instance types. Now you can configure a wider variety of instance types and be confident that Elastigroup optimizes the traffic distribution.
How it Works
The illustration below provides a high-level example of the method ITF uses for weighting the distribution of traffic to the target groups.
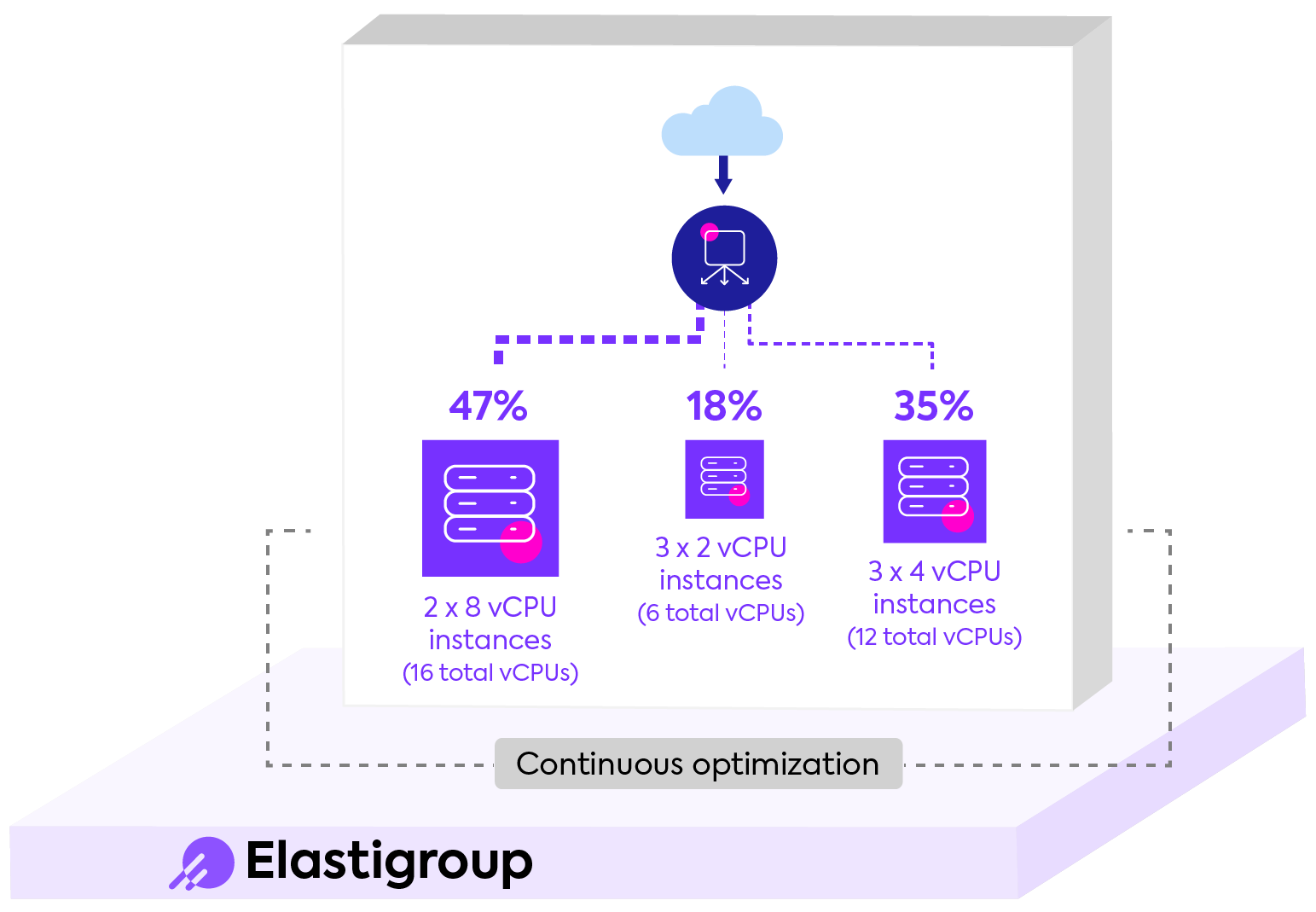
In this example, ITF has created three target groups. From left to right:
- Target Group 1 has two instances, each having eight vCPUs, making a total of 16 vCPUs for the target group.
- Target Group 2 has three instances, each having two vCPUs, making a total of six vCPUs for the target group.
- Target Group 3 has three instances, each having four vCPUs, making a total of 12 vCPUs for the target group.
ITF calculates distribution weights as a percentage based on the target groups’s vCPUs per total vCPUs of all the target groups. For example:
Weight of Target Group 1 = (16 vCPU/34 vCPU) * 100 = 47%
The weights are used to ensure that whatever the capacity of the instances, each instance will be utilized to the appropriate amount. This method of load-balancing inbound traffic across varied instance types and sizes guarantees optimal workload performance and infrastructure utilization.